GLAUCOMA
Glaucoma the sneak Thief of sight is a disease that damages your eye's optic nerve and cause blindness it is untreated. A person over 60, diabetes, high blood pressure and heart disease patients or one with family history of glaucoma is at high risk of glaucoma.
How optical nerve gets damaged?
* There are two segments in the eyes:
1. Anterior segment: Area from the back of the cornea to the lens it again divided into two anterior chamber (back of the cornea to the front of the Iris) and posterior chamber (back of the Iris to the front of the lens)
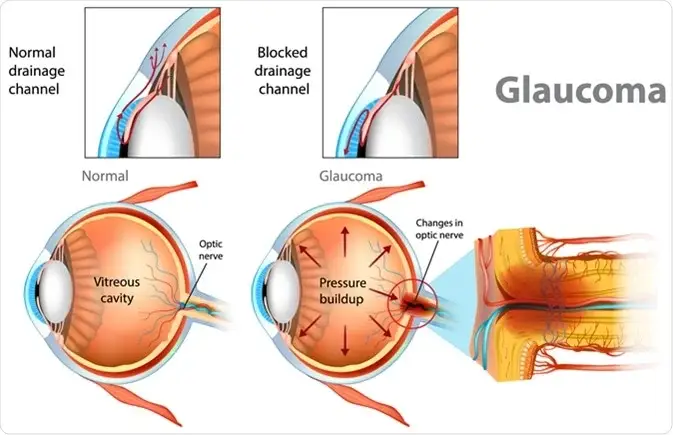
2. Posterior segment area behind the crystalline lens anterior segment is filled with a fluid known as aqueous humor. Ciliary epithelium Aqueous humors from blood plasma and enter into the anterior and posterior chamber then it drain out into the episcleral vein through trabecular meshwork and schemes canal. Our eye constantly makes aqueous humor as a new aqueous amount should drain out the fluid drains out through an area called the drainage angle. This process keeps pressure in the eyes (IOP) Stable.
But if the drainage angle is not working properly or the amount of fluid production increases the fluid builds up and pressure inside the eyes Rises damaging the optical nerve so there is a peripheral vision loss ( tunnel vision) and it get worse over time.
Glaucoma who's at risk?
- Age: people over 60
- Family History: Having family members with glaucoma
- Race: African Americans are more likely to get glaucoma and suffer permanent vision loss then Caucasian (white people).
- Ocular hypertension: It is a condition where the pressure in your eyes or lop is too high. High pressure within I scan eventually damage the optic nerve and lead to glaucoma permanent vision loss.
- Severe myopia: It is associated with in increase the risk of pathological ocular complications may lead to building disorders like glaucoma.
- Physical injuries to the eyes: Severe trauma can result in immediate increased eye pressure and future increase in pressure due internal damage injury also can dislocate the lens closing the drainage angle and increasing Pressure.
- Ocular surgery: Can cause a change in the eye's pressure. It can be treated with medicines.
- Medical conditions: Diabetes high blood pressure and heart disease may increase the risk of developing glaucoma.
- Corticosteroid uses: Prolonged use may increase the risk of setting secondary glaucoma. Corticosteroid medicines are used to provide relief for the inflamed area of the body. They are often used as part of treatment for different diseases such as severe allergies or skin problems, asthma or arthritis. While using these medicines they want to check their IOP twice a year.
- Migraine: prolonged increased pressure can lead to visual loss if not corrected.
- Other eye related risk factors: corneal Thickness and optic nerve appearance indicate risk for development of glaucoma conditions such as retinal detachment, eye tumors and eye inflammation may also induce glaucoma.
Types of glaucoma
Two types
- Congenital glaucoma
- Acquired glaucoma
1. Congenital glaucoma:
It is a rare disease when a congenital defect in the angle of anterior chamber which obstruct the flow of aqueous humor IOP will increase due to fluid buildup if it is untreated the optic nerve become damaged in most cases surgery is required.
It again divided into 3:-
- True congenital glaucoma: Raised IOP during intrauterine eye and child is born with ocular enlargement.
- Infantile glaucoma: When the disease manifest prior to the child's 3rd birthday.
- Juvenile glaucoma: Who develop pressure rise between 3 to 6 years of eye
2. Acquired glaucoma
It again divided into 2:-
- Primary glaucoma
- Secondary glaucoma
1. Primary Glaucoma
In primary glaucoma there are
- Primary open angled glaucoma.
- Primary angle closure glaucoma
1. Primary open angle glaucoma (POAG)
- This is the most common form of glaucoma.
- It occurs when the fluid drainage is poor and fluid buildup in the eyes and the internal eye pressure goes up.
- This increased pressure can cause damage to the optic nerve and vision loss.
- The exact mechanism of damage is still unknown.
- This type of glaucoma is painless and caused no vision changes at first.
- Some people can have optic nerve that are sensitive to normal eye pressure this means there is risk of getting glaucoma is higher than normal regular eye exams are important to find early signs of damage to their optic nerve.
POAG develops gradually and painlessly and has no initial symptoms vision is normal in the early stages.
As the disease progresses, blind spot develop in your peripheral side vision is untreated peripheral or side mission is slowly lost.
Tunnel Vision: Defective sight in which objects cannot be properly seen if not close to the Centre of the field of view
* Eventually all vision may lost.
2. Primary angle closure glaucoma (PACG)
- Also called closed angle glaucoma or narrow angle glaucoma
- This type of glaucoma is an emergency situation
- It occurs when the Iris block the drainage ankle and results in fluid builds up in the anterior chamber and increase in pressure.
When the drainage angle gets completely blocked eye pressure Rises very quickly. This is called an acute attack it is a true emergency situation.
-
Many people with angle closure glaucoma develop it slowly this is called chronic angle closure glaucoma the art no symptoms at first so they don't know they have it until the damage is severe or they have an attack.
- Angle closure glaucoma can cause blindness if not treated.
Symptoms of PACG
- Severe eye pain in eye.
- Redness of the eye
- Decreased vision or Blurred vision
- Seeing rainbows or Halos
- Headache
- Nausea
- Vomiting
2.Secondary glaucoma
Glaucoma can develop as a complication from other condition including:
- * Eye injuries
- * Diabetes
- * Steroid use cortisteroid asthma arthritis etc.
- * High blood pressure
Normal tension glaucoma
Glaucoma can develop as a complication from other condition including:
- * No tension on normal tension glaucoma is not has common
- * in these cases the eyes pressure is within the normal range but the optic nerve still set damaged and also blind spots in the peripheral side vision is seen.
- *The exact mechanism of damage is still unknown.
Who is considered has "glaucoma suspects”?
Some people have no sign of damage but IOP intraocular pressure is higher than the normal range these patients are considered as a glaucoma suspect they have a higher risk of eventually developing glaucoma. Some people are considered glaucoma suspect even if their lOP is at normal range because their ophthalmologist May notice something different about their optical nerve. Glaucoma suspect have no symptoms that is why glaucoma suspect want to monitor their eyes carefully so changes can be noticed and begin treatment if needed.
Glaucoma diagnosis
* An eye pressure checkup not only needed to find glaucoma.
Common tests to diagnose glaucoma
- Tonometry: to measure your eye pressure
- Ophthalmoscopy: To examine your optic disc optic nerve and retinal parameters after dilation of the eye.
- Gonioscopy: Inspect your eyes drainage angle
- Perimetry: To test your peripheral (side) vision for visual field examination test.
- Pachymetry: To measure your retinal Thickness
- OCT: Optical coherence tomography, to measure RNFL thickness ( RNFL : retinal nerve fiber layer)
Can glaucoma be stopped?
Glaucoma damage is permanent it cannot be reversed but medicine and surgery help to stop further damage.
Medical management
Glaucoma can be controlled with eye drop medicine this reduce eye pressure or reduce the amount of Aqueous humor production other reduced pressure by helping fluid flow better through the drainage angle.
-
BETA Adrenergic blockers: timolol, betaxolol, are used to decrease aqueous humor production.
-
Cholinergic (Miotics): pilocarpine, carbacol are used to reduce IOP by facilitating the outflow of aqueous humor.
-
Carbonic Anhydrase inhibitors: Dorzolamide, methazolamide Or accetazolamide to decrease the formation and secretion of aqueous humor.
-
Prostaglandin Analogs: latanoprost to reduce IOP by increasing uveoscleral outflow.
Surgical Management
There are 2 main type of laser surgery to treat glaucoma. The help aqueous drain from the eye.
1: Argon Laser Trabeculoplasty.
- * used to treat open angle glaucoma
- * In this thermal argon laser burns are applied to the inner surface of trabecular meshwork the intra color spaces and widen the canal of Schulman therapy increases the outflow of aqueous humor and decreasing the IOP.
2. Laser Iridotomy
- * used to treat angle closure glaucoma
- * an opening is made by the laser beam in the Iris to eliminate the pupillary block this hole help fluid flow to the drainage angle and reveals pressure by promoting outflow of the aqueous humor.
There are some operating room surgeries also
1) Cyclocryotherapy
Application of a freezing probe to the sclera over the ciliary body that destroy some of the ciliary processes result in the production of the amount of aqueous humor produced.
2) Cyclodialysis
Through a small inclusion in the sclera is Spatula type instrument is passed into the anterior chamber creating an opening in the angle.
3) Trabeculotomy
A tiny flap is created in the sclera and further section of sclera removed to the produce an opening your surgeon will also create a bubble like a pocket in the conjunctive called a filtration bleb. It is usually hidden under the upper eyelid and cannot be seen aqueous humor will be able to drain out the eye through the flap and into the bleb. In the bleb fluid is absorbed by tissue around your eye and lowering eye pressure.
“Glaucoma is a silent Thief of sight”
Glaucoma has no symptoms in its early stages in fact half of the people with glaucoma don't know they have it. Having regular I exams can help your Ophthalmologist find this disease before you lose vision. Glaucoma is not curable and vision lost cannot be regained more than 3 million people in the United States have glaucoma it is the second leading cause of blindness in the world it can take as much as 40 % of vision without a person’s noticing. Without regular I exams you good lose vision to glaucoma before you know you have it. Annual exams allow doctors to check for common diseases eye asses how your eyes work together and evaluate your eyes has an indicator of your overall health. Lifestyle changes may help to control high eye pressure or promote eye health. Eat healthy diet (vitamins and zinc exercise) for eyes etc.
“Don't wait for warning signs; a dilated eye exam can detect glaucoma early and save your site”

Safeela Nasree M.
B.Voc Optometry Final Year Student,
ITEES College of Health Sciences
April 23, 2022